Unbundling the Graph in GraphRAG – O’Reilly
One in style time period encountered in generative AI observe is retrieval-augmented era (RAG). Causes for utilizing RAG are clear: giant language fashions (LLMs), that are successfully syntax engines, are likely to “hallucinate” by inventing solutions from items of their coaching information. The haphazard outcomes could also be entertaining, though not fairly based mostly in truth. RAG offers a solution to “floor” solutions inside a specific set of content material. Additionally, instead of costly retraining or fine-tuning for an LLM, this strategy permits for fast information updates at low value. See the first sources “REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training” by Kelvin Guu, et al., at Google, and “Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks” by Patrick Lewis, et al., at Fb—each from 2020.
Right here’s a easy tough sketch of RAG:
- Begin with a set of paperwork a few area.
- Cut up every doc into chunks.
- Run every chunk of textual content by way of an embedding mannequin to compute a vector for it.
- Retailer these chunks in a vector database, listed by their embedding vectors.
When a query will get requested, run its textual content by way of this identical embedding mannequin, decide which chunks are nearest neighbors, then current these chunks as a ranked record to the LLM to generate a response. Whereas the general course of could also be extra sophisticated in observe, that is the gist.
The varied flavors of RAG borrow from recommender methods practices, corresponding to the usage of vector databases and embeddings. Massive-scale manufacturing recommenders, search engines like google and yahoo, and different discovery processes even have an extended historical past of leveraging data graphs, corresponding to at Amazon, Alphabet, Microsoft, LinkedIn, eBay, Pinterest, and so forth.
What’s GraphRAG?
Graph applied sciences assist reveal nonintuitive connections inside information. For instance, articles about former US Vice President Al Gore may not focus on actor Tommy Lee Jones, though the 2 have been roommates at Harvard and began a rustic band collectively. Graphs enable for searches throughout a number of hops—that’s, the flexibility to discover neighboring ideas recursively—corresponding to figuring out hyperlinks between Gore and Jones.
GraphRAG is a method that makes use of graph applied sciences to boost RAG, which has develop into popularized since Q3 2023. Whereas RAG leverages nearest neighbor metrics based mostly on the relative similarity of texts, graphs enable for higher recall of much less intuitive connections. The names “Tommy Lee Jones” and “Al Gore” will not be embedded as related textual content, relying in your coaching corpus for RAG, however they could possibly be linked by way of a data graph. See the 2023 article which seems to be the origin of this idea, “NebulaGraph Launches Industry-First Graph RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation with LLM Based on Knowledge Graphs,” plus a very good current survey paper, “Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey” by Boci Peng, et al.
That stated, the “graph” a part of GraphRAG means a number of various things—which is probably one of many extra essential factors right here to know. One solution to construct a graph to make use of is to attach every textual content chunk within the vector retailer with its neighbors. The “distance” between every pair of neighbors could be interpreted as a chance. When a query immediate arrives, run graph algorithms to traverse this probabilistic graph, then feed a ranked index of the collected chunks to LLM. That is a part of how the Microsoft GraphRAG strategy works.
One other strategy leverages a area graph of associated area data, the place nodes within the graph symbolize ideas and hyperlink to textual content chunks within the vector retailer. When a immediate arrives, convert it right into a graph question, then take nodes from the question end result and feed their string representations together with associated chunks to the LLM.
Going a step additional, some GraphRAG approaches make use of a lexical graph by parsing the chunks to extract entities and relations from the textual content, which enhances a area graph. Convert an incoming immediate to a graph question, then use the end result set to pick out chunks for the LLM. Good examples are described within the GraphRAG Manifesto by Philip Rathle at Neo4j.
There are at the very least two methods to map from a immediate to pick out nodes within the graph. On the one hand, Neo4j and others generate graph queries. However, it’s attainable to generate a textual content description for every node within the graph, then run these descriptions by way of the identical embedding mannequin used for the textual content chunks. This latter strategy with node embeddings could be extra strong and doubtlessly extra environment friendly.
Yet one more embellishment is to make use of a graph neural community (GNN) educated on the paperwork. GNNs generally get used to deduce nodes and hyperlinks, figuring out the doubtless “lacking” components of a graph. Researchers at Google claim this method outperforms different GraphRAG approaches whereas needing much less compute assets, through the use of GNNs to re-rank essentially the most related chunks introduced to the LLM.
There are a number of different makes use of of the phrase “graph” in LLM-based purposes, and lots of of those tackle the controversy about whether or not LLMs can cause. For instance, “Graph of Thoughts” by Maciej Besta, et al., decomposes a fancy job right into a graph of subtasks, then makes use of LLMs to reply the subtasks whereas optimizing for prices throughout the graph. Different works leverage completely different types of graph-based reasoning, for instance “Barack’s Wife Hillary: Using Knowledge-Graphs for Fact-Aware Language Modeling” by Robert Logan, et al., makes use of LLMs to generate a graph of logical propositions. Questions get answered based mostly on logical inference from these extracted details. One in every of my current favorites is “Implementing GraphReader with Neo4j and LangGraph” by Tomaz Bratanic, the place GraphRAG mechanisms acquire a “pocket book” of potential parts for composing a response. What’s previous turns into new once more: Substitute the time period “pocket book” with “blackboard” and “graph-based agent” with “management shell” to return to the blackboard system architectures for AI from the Nineteen Seventies–Nineteen Eighties. See the Hearsay-II project, BB1, and plenty of papers by Barbara Hayes-Roth and colleagues.
Does GraphRAG enhance outcomes?
How a lot do GraphRAG approaches enhance over RAG? Papers quantifying the evaluation of raise have been rising over the previous few months. “GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation” by Yuntong Hu, et al., at Emory reported that their graph-based strategy “considerably outperforms present state-of-the-art RAG strategies whereas successfully mitigating hallucinations.” To quantify this raise, “TRACE the Evidence: Constructing Knowledge-Grounded Reasoning Chains for Retrieval-Augmented Generation” by Jinyuan Fang, et al., introduced the TRACE framework for measuring outcomes, which confirmed how GraphRAG achieves a median efficiency enchancment of as much as 14.03%. Equally, “Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Knowledge Graphs for Customer Service Question Answering” by Zhentao Xu, et al., reported that GraphRAG in LinkedIn customer support diminished median per-issue decision time by 28.6%.
Nonetheless, one drawback lingers inside the GraphRAG house. The favored open supply libraries and a lot of the vendor options promote a normal notion that the “graph” in GraphRAG will get generated routinely by an LLM. These don’t make affordances for utilizing preexisting data graphs, which can have been rigorously curated by area consultants. In some instances, data graphs should be constructed utilizing ontologies (corresponding to from NIST) as guardrails or for different issues.
Individuals who work in regulated environments (assume: public sector, finance, healthcare, and many others.) are likely to dislike utilizing an AI software as a “black field” resolution, which magically handles work which will want human oversight. Think about entering into entrance of a choose to hunt a warrant and explaining, “Your honor, a LLM collected the proof, plus or minus a number of hallucinations.”
Whereas LLMs could be highly effective for summarizing the important thing factors from many paperwork, they aren’t essentially one of the best ways to deal with many sorts of duties. “A Latent Space Theory for Emergent Abilities in Large Language Models” by Hui Jiang presents a statistical rationalization for emergent LLM talents, exploring a relationship between ambiguity in a language versus the dimensions of fashions and their coaching information. “Do LLMs Really Adapt to Domains? An Ontology Learning Perspective” by Huu Tan Mai, et al., confirmed how LLMs don’t cause constantly about semantic relationships between ideas, and as an alternative are biased by the framing of their coaching examples. General the current paper “Hype, Sustainability, and the Price of the Bigger-is-Better Paradigm in AI” by Gaël Varoquaux, Sasha Luccioni, and Meredith Whittaker explores how LLMs present diminishing returns as information and mannequin sizes scale, in distinction to the scaling laws which recommend a “greater is best” assumption.
One of many root causes for failures in graphs generated by LLMs includes the matter of entity resolution. In different phrases, how properly are the “ideas”—represented by the nodes and edges of a graph—disambiguated inside the context of the area? For instance, a point out of “NLP” may check with pure language processing in a single context or neural linguistic programming in one other. LLMs are infamous for making these sorts of errors when producing graphs. These “misconceptions” accumulate into bigger errors as an algorithm traverses the hops throughout a graph, looking for details to feed to an LLM. For instance, “Bob E. Smith” and “Bob R. Smith” are most likely not the identical particular person, regardless that their names differ by one letter. However, “al-Hajj Abdullah Qardash”and “Abu ‘Abdullah Qardash Bin Amir” stands out as the identical particular person, owing to the assorted conventions of transliterating Arabic names into English.
Entity decision merges the entities which seem constantly throughout two or extra structured information sources, whereas preserving proof selections. These entities could symbolize folks, organizations, maritime vessels, and so forth, and their names, addresses, or different personally figuring out data (PII) is used as options for entity decision. The issue of evaluating textual content options to keep away from false positives or false negatives tends to have many troublesome edge instances. Nonetheless, the core worth of entity decision in software areas corresponding to voter registration or passport management is whether or not the sting instances get dealt with appropriately. When names and addresses have been transliterated from Arabic, Russian, or Mandarin, as an example, the sting instances in entity decision develop into much more troublesome, since cultural conventions dictate how we should interpret options.
A generalized, unbundled workflow
A extra accountable strategy to GraphRAG is to unbundle the method of data graph development, paying particular consideration to information high quality. Begin with any required schema or ontology as a foundation, and leverage structured information sources to create a “spine” for organizing the graph, based mostly on entity decision. Then join the graph nodes and relations extracted from unstructured information sources, reusing the outcomes of entity decision to disambiguate phrases inside the area context.
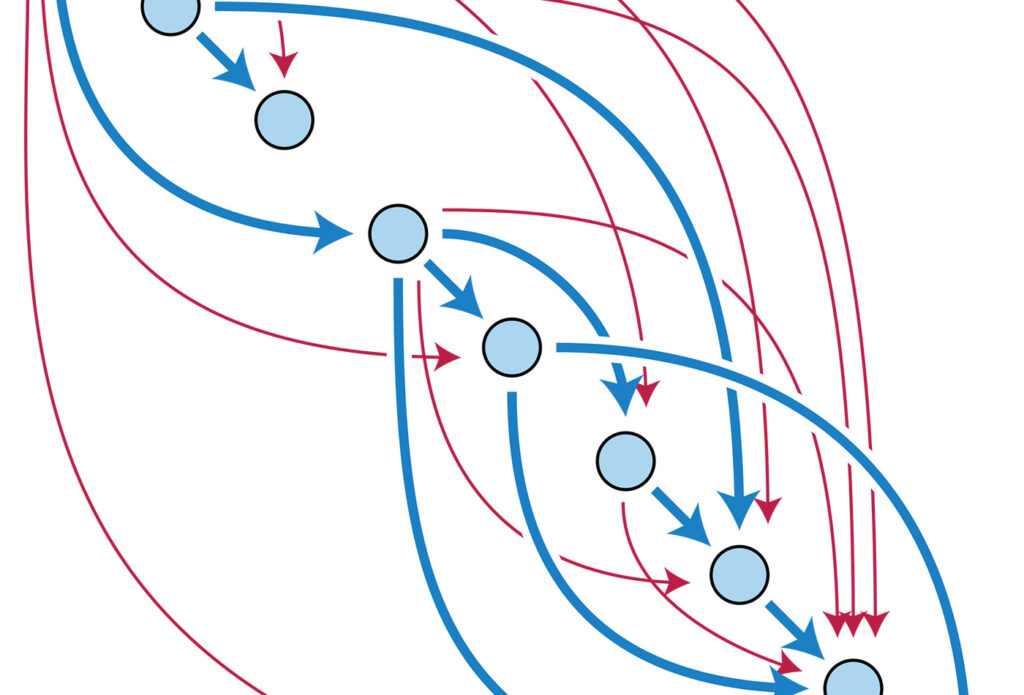
A generalized workflow for this unbundled strategy is proven under, with a path alongside the highest to ingest structured information plus schema, and a path alongside the underside to ingest unstructured information:

The outcomes on the appropriate aspect are textual content chunks saved in a vector database, listed by their embeddings vectors, plus a mixed area graph and lexical graph saved in a graph database. The weather of both retailer are linked collectively. By the numbers:
- Run entity decision to determine the entities which happen throughout a number of structured information sources.
- Import your information data right into a graph, utilizing any ontology (or taxonomy, managed vocabularies, schema, and many others.) that’s required in your use case.
- Should you already had a curated data graph, you then’re merely accumulating new nodes and relations into it.
- Overlay the entity decision outcomes as nodes and edges connecting the information data, to disambiguate the place there may be a number of nodes in a graph for a similar logical entity.
- Reuse the entity decision outcomes to customise an entity linker for the area context of your use case (see under).
- Chunk your paperwork from unstructured information sources, as normal in GraphRAG.
- Run the textual content chunks by way of NLP parsing, extracting attainable entities (noun phrases) utilizing named entity recognition after which an entity linker to hook up with beforehand resolved entities.
- Hyperlink the extracted entities to their respective textual content chunks.
This strategy fits the wants of enterprise use instances on the whole, leveraging “smaller” albeit state-of-the-art fashions and permitting for human suggestions at every step, whereas preserving the proof used and selections made alongside the way in which. Oddly sufficient, this will additionally make updates to the graph less complicated to handle.
When a immediate arrives, the GraphRAG software can observe two complementary paths to find out which chunks to current to the LLM. That is proven within the following:

A set of open supply tutorials function a reference implementation for this strategy. Utilizing open information about companies within the Las Vegas metro space in the course of the pandemic, “Entity Resolved Knowledge Graphs: A Tutorial” explores how one can use entity decision to merge three datasets about PPP loan fraud for setting up a data graph in Neo4j. Clair Sullivan prolonged this instance in “When GraphRAG Goes Bad: A Study in Why You Cannot Afford to Ignore Entity Resolution” utilizing LangChain to supply a chatbot to discover potential fraud instances.
A 3rd tutorial, “How to Construct Knowledge Graphs from Unstructured Data,” exhibits how one can carry out the generalized workflow above for extracting entities and relations from unstructured information. This leverages state-of-the-art open fashions (corresponding to GLiNER for named entity recognition) and in style open supply libraries corresponding to spaCy and LanceDB (see the code and slides). Then a fourth tutorial, “Panama Papers Investigation using Entity Resolution and Entity Linking,” by Louis Guitton, makes use of entity decision outcomes to customise an entity linker based mostly on spaCy NLP pipelines, and is obtainable as a Python library. This exhibits how structured and unstructured information sources could be blended inside a data graph based mostly on area context.
Abstract
General, GraphRAG approaches enable for extra refined retrieval patterns than utilizing vector databases alone for RAG—leading to higher LLM outcomes. Early examples of GraphRAG used LLMs to generate graphs automagically, and though we’re working to keep away from hallucinations, these automagical components introduce miscomprehensions.
An unbundled workflow replaces the “magic” with a extra accountable course of whereas leveraging state-of-the-art “smaller” fashions at every step. Entity decision is a core part, offering means for mixing collectively the structured and unstructured information based mostly on proof, and observing difficult cultural norms to know the figuring out options within the information.
Let’s revisit the purpose about RAG borrowing from recommender methods. LLMs solely present one piece of the AI puzzle. For instance, they’re nice for summarization duties, however LLMs have a tendency to interrupt down the place they should disambiguate rigorously amongst ideas in a particular area. GraphRAG brings in graph applied sciences to assist make LLM-based purposes extra strong: conceptual illustration, illustration studying, graph queries, graph analytics, semantic random walks, and so forth. Consequently, GraphRAG mixes two our bodies of “AI” analysis: the extra symbolic reasoning which data graphs symbolize and the extra statistical approaches of machine studying. Going ahead there’s lots of room for “hybrid AI” approaches that mix the perfect of each, and GraphRAG might be simply the tip of the iceberg. See the superb discuss “Systems That Learn and Reason” by Frank van Harmelen for extra exploration about hybrid AI tendencies.
This text is predicated on an early discuss, “Understanding Graph RAG: Enhancing LLM Applications Through Knowledge Graphs.” Listed below are another beneficial assets on this matter: