Strong and environment friendly medical imaging with self-supervision – Google AI Weblog

Regardless of latest progress within the subject of medical artificial intelligence (AI), most present fashions are narrow, single-task programs that require giant portions of labeled knowledge to coach. Furthermore, these fashions can’t be simply reused in new scientific contexts as they typically require the gathering, de-identification and annotation of site-specific knowledge for each new deployment surroundings, which is each laborious and expensive. This drawback of data-efficient generalization (a mannequin’s capacity to generalize to new settings utilizing minimal new knowledge) continues to be a key translational problem for medical machine studying (ML) fashions and has in flip, prevented their broad uptake in actual world healthcare settings.
The emergence of foundation models gives a big alternative to rethink growth of medical AI to make it extra performant, safer, and equitable. These fashions are educated utilizing knowledge at scale, typically by self-supervised studying. This course of leads to generalist fashions that may quickly be tailored to new duties and environments with much less want for supervised knowledge. With basis fashions, it could be potential to soundly and effectively deploy fashions throughout varied scientific contexts and environments.
In “Robust and Efficient MEDical Imaging with Self-supervision” (REMEDIS), to be revealed in Nature Biomedical Engineering, we introduce a unified large-scale self-supervised studying framework for constructing basis medical imaging fashions. This technique combines giant scale supervised transfer learning with self-supervised learning and requires minimal task-specific customization. REMEDIS reveals important enchancment in data-efficient generalization throughout medical imaging duties and modalities with a 3–100x discount in site-specific knowledge for adapting fashions to new scientific contexts and environments. Constructing on this, we’re excited to announce Medical AI Research Foundations (hosted by PhysioNet), an enlargement of the general public launch of chest X-ray Foundations in 2022. Medical AI Analysis Foundations is a set of open-source non-diagnostic fashions (beginning with REMEDIS fashions), APIs, and assets to assist researchers and builders speed up medical AI analysis.
Massive scale self-supervision for medical imaging
REMEDIS makes use of a mixture of pure (non-medical) pictures and unlabeled medical pictures to develop sturdy medical imaging basis fashions. Its pre-training technique consists of two steps. The primary entails supervised illustration studying on a large-scale dataset of labeled pure pictures (pulled from Imagenet 21k or JFT) utilizing the Big Transfer (BiT) technique.
The second step entails intermediate self-supervised studying, which doesn’t require any labels and as a substitute, trains a mannequin to study medical knowledge representations independently of labels. The particular method used for pre-training and studying representations is SimCLR. The strategy works by maximizing settlement between in a different way augmented views of the identical coaching instance by way of a contrastive loss in a hidden layer of a feed-forward neural community with multilayer perceptron (MLP) outputs. Nonetheless, REMEDIS is equally suitable with different contrastive self-supervised studying strategies. This coaching technique is relevant for healthcare environments as many hospitals purchase uncooked knowledge (pictures) as a routine observe. Whereas processes must be applied to make this knowledge usable inside fashions (i.e., affected person consent previous to gathering the information, de-identification, and so on.), the pricey, time-consuming, and tough process of labeling that knowledge might be averted utilizing REMEDIS.
 |
| REMEDIS leverages large-scale supervised studying utilizing pure pictures and self-supervised studying utilizing unlabeled medical knowledge to create sturdy basis fashions for medical imaging. |
Given ML mannequin parameter constraints, it can be crucial that our proposed method works when utilizing each small and huge mannequin structure sizes. To review this intimately, we thought of two ResNet architectures with generally used depth and width multipliers, ResNet-50 (1×) and ResNet-152 (2×) because the spine encoder networks.
After pre-training, the mannequin was fine-tuned utilizing labeled task-specific medical knowledge and evaluated for in-distribution process efficiency. As well as, to judge the data-efficient generalization, the mannequin was additionally optionally fine-tuned utilizing small quantities of out-of-distribution (OOD) knowledge.
Analysis and outcomes
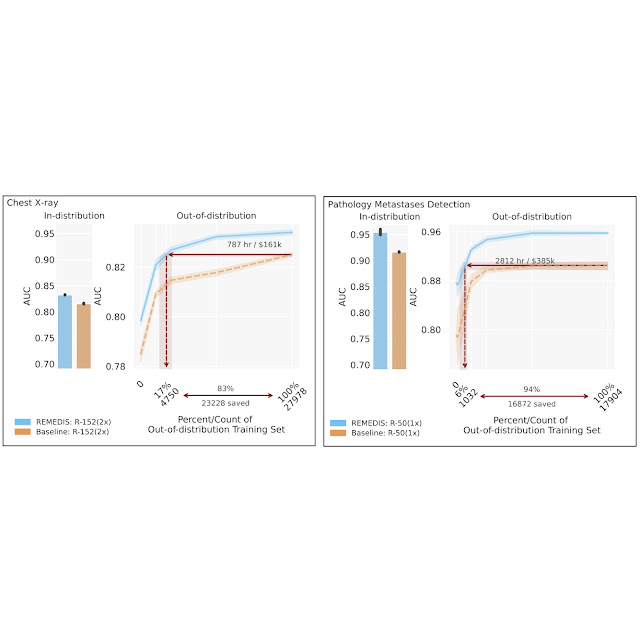
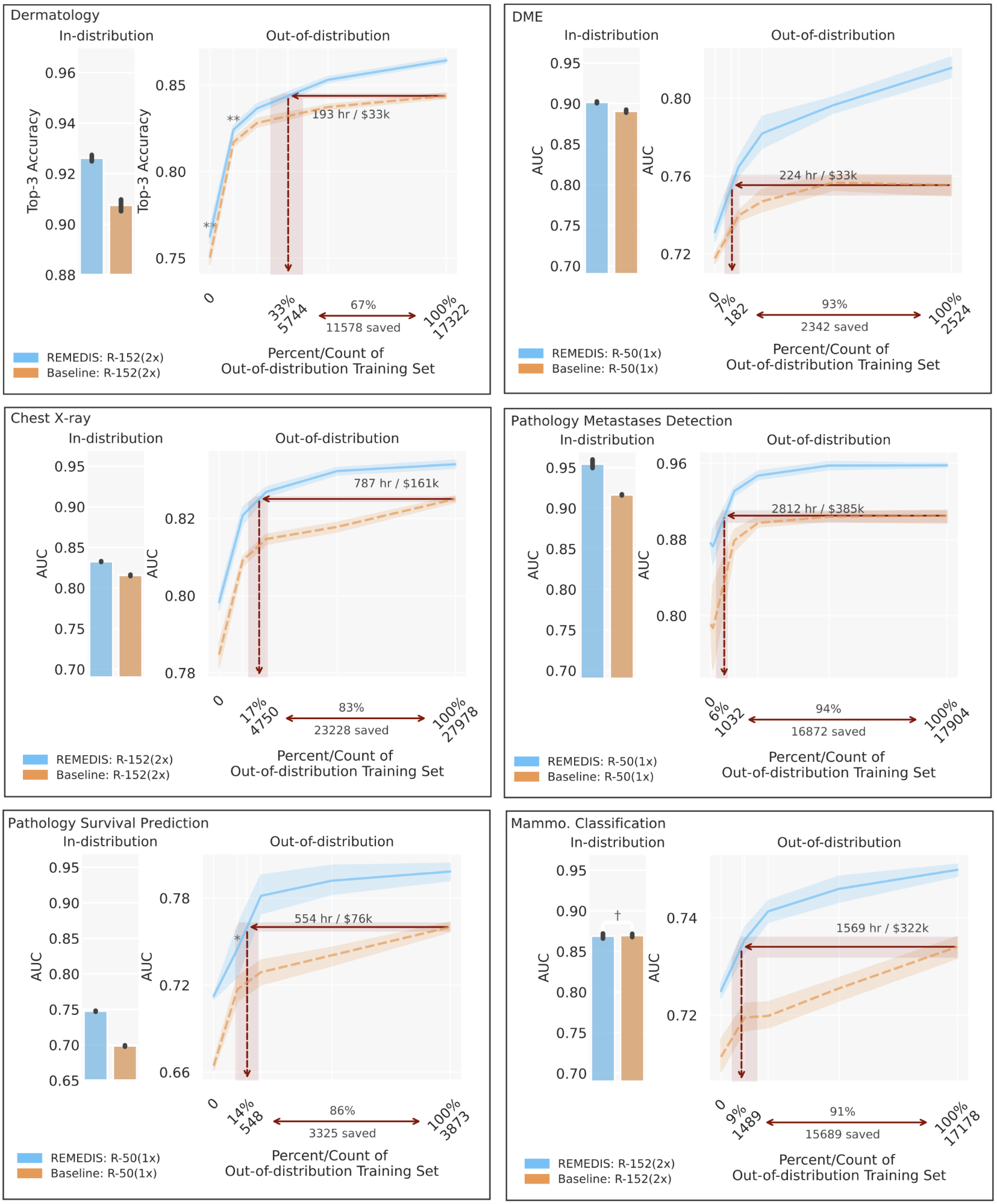
To guage the REMEDIS mannequin’s efficiency, we simulate life like eventualities utilizing retrospective de-identified knowledge throughout a broad vary of medical imaging duties and modalities, together with dermatology, retinal imaging, chest X-ray interpretation, pathology and mammography. We additional introduce the notion of data-efficient generalization, capturing the mannequin’s capacity to generalize to new deployment distributions with a considerably lowered want for knowledgeable annotated knowledge from the brand new scientific setting. In-distribution efficiency is measured as (1) enchancment in zero-shot generalization to OOD settings (assessing efficiency in an OOD analysis set, with zero entry to coaching knowledge from the OOD dataset) and (2) important discount within the want for annotated knowledge from the OOD settings to succeed in efficiency equal to scientific consultants (or threshold demonstrating scientific utility). REMEDIS reveals considerably improved in-distribution efficiency with as much as 11.5% relative enchancment in diagnostic accuracy over a strongly supervised baseline.
Extra importantly, our technique results in data-efficient generalization of medical imaging fashions, matching sturdy supervised baselines leading to a 3–100x discount within the want for retraining knowledge. Whereas SimCLR is the first self-supervised studying method used within the research, we additionally present that REMEDIS is suitable with different approaches, similar to MoCo-V2, RELIC and Barlow Twins. Moreover, the method works throughout mannequin structure sizes.
 |
| REMEDIS is suitable with MoCo-V2, RELIC and Barlow Twins as alternate self-supervised studying methods. All of the REMEDIS variants result in data-efficient generalization enhancements over the sturdy supervised baseline for dermatology situation classification (T1), diabetic macular edema classification (T2), and chest X-ray situation classification (T3). The grey shaded space signifies the efficiency of the sturdy supervised baseline pre-trained on JFT. |
Medical AI Analysis Foundations
Constructing on REMEDIS, we’re excited to announce Medical AI Research Foundations, an enlargement of the general public launch of chest X-ray Foundations in 2022. Medical AI Analysis Foundations is a repository of open-source medical basis fashions hosted by PhysioNet. This expands the earlier API-based method to additionally embody non-diagnostic fashions, to assist researchers and builders speed up their medical AI analysis. We consider that REMEDIS and the discharge of the Medical AI Analysis Foundations are a step towards constructing medical fashions that may generalize throughout healthcare settings and duties.
We’re seeding Medical AI Analysis Foundations with REMEDIS fashions for chest X-ray and pathology (with associated code). Whereas the present chest X-ray Basis method focuses on offering frozen embeddings for application-specific nice tuning from a mannequin educated on a number of giant personal datasets, the REMEDIS fashions (educated on public datasets) allow customers to fine-tune end-to-end for his or her software, and to run on native gadgets. We suggest customers take a look at totally different approaches primarily based on their distinctive wants for his or her desired software. We count on so as to add extra fashions and assets for coaching medical basis fashions similar to datasets and benchmarks sooner or later. We additionally welcome the medical AI analysis group to contribute to this.
Conclusion
These outcomes recommend that REMEDIS has the potential to considerably speed up the event of ML programs for medical imaging, which may protect their sturdy efficiency when deployed in a wide range of altering contexts. We consider this is a crucial step ahead for medical imaging AI to ship a broad impression. Past the experimental outcomes offered, the method and insights described right here have been built-in into a number of of Google’s medical imaging research projects, similar to dermatology, mammography and radiology amongst others. We’re utilizing an analogous self-supervised studying method with our non-imaging basis mannequin efforts, similar to Med-PaLM and Med-PaLM 2.
With REMEDIS, we demonstrated the potential of basis fashions for medical imaging purposes. Such fashions maintain thrilling prospects in medical purposes with the chance of multimodal illustration studying. The observe of medication is inherently multimodal and incorporates info from pictures, digital well being information, sensors, wearables, genomics and extra. We consider ML programs that leverage these knowledge at scale utilizing self-supervised studying with cautious consideration of privateness, security, equity and ethics will assist lay the groundwork for the subsequent era of studying well being programs that scale world-class healthcare to everybody.
Acknowledgements
This work concerned in depth collaborative efforts from a multidisciplinary staff of researchers, software program engineers, clinicians, and cross-functional contributors throughout Google Well being AI and Google Mind. Particularly, we want to thank our first co-author Jan Freyberg and our lead senior authors of those initiatives, Vivek Natarajan, Alan Karthikesalingam, Mohammad Norouzi and Neil Houlsby for his or her invaluable contributions and assist. We additionally thank Lauren Winer, Sami Lachgar, Yun Liu and Karan Singhal for his or her suggestions on this submit and Tom Small for assist in creating the visuals. Lastly, we additionally thank the PhysioNet staff for his or her assist on internet hosting Medical AI Analysis Foundations. Customers with questions can attain out to medical-ai-research-foundations at google.com.