Combining Information Administration and Information Storytelling to Generate Worth
These days, I’ve been specializing in knowledge storytelling and its significance in successfully speaking the outcomes of information evaluation to generate worth. Nevertheless, my technical background, which may be very near the world of information administration and its issues, pushed me to mirror on what knowledge administration wants to make sure you can construct data-driven tales shortly. I got here to a conclusion that’s usually taken as a right however is all the time good to bear in mind. You’ll be able to’t rely solely on knowledge to construct data-driven tales. It’s also essential for an information administration system to contemplate not less than two facets. Do you wish to know which of them? Let’s attempt to discover out on this article.
What we’ll cowl on this article:
- Introducing Information
- Information Administration Techniques
- Information Storytelling
- Information Administration and Information Storytelling
1. Introducing Information
We frequently speak about, use, and generate knowledge. However have you ever puzzled what knowledge is and what sorts of knowledge exist? Let’s attempt to outline it.
Information is uncooked information, numbers, or symbols that may be processed to generate significant info. There are various kinds of knowledge:
- Structured knowledge is knowledge organized in a set schema, comparable to SQL or CSV. The primary execs of this kind of knowledge are that it’s simple to derive insights. The primary disadvantage is that schema dependence limits scalability. A database is an instance of this kind of knowledge.
- Semi-structured knowledge is partially organized and not using a fastened schema, comparable to JSON XML. The professionals are that they’re extra versatile than structured knowledge. The primary cons is that the meta-level construction might include unstructured knowledge. Examples are annotated textual content, comparable to tweets with hashtags.
- Unstructured knowledge, comparable to audio, video, and textual content, should not annotated. The primary execs are that they’re unstructured, so it’s simple to retailer them. They’re additionally very scalable. Nevertheless, they’re difficult to handle. For instance, it’s troublesome to extract which means. Plain textual content and digital pictures are examples of unstructured knowledge.
To prepare knowledge whose quantity is growing over time, it’s important to handle them correctly.
2. Information Administration
Information administration is the follow of ingesting, processing, securing, and storing a corporation’s knowledge, which is then utilized for strategic decision-making to enhance enterprise outcomes [1]. There are three central knowledge administration programs:
- Information Warehouse
- Information Lake
- Information Lakehouse
2.1 Information Warehouse
An information warehouse can deal with solely structured knowledge post-extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes. As soon as elaborated, the info can be utilized for reporting, dashboarding, or mining. The next determine summarizes the construction of an information warehouse.

Fig. 1: The structure of an information warehouse
The primary issues with knowledge warehouses are:
- Scalability – they aren’t scalable
- Unstructured knowledge – they don’t handle unstructured knowledge
- Actual-time knowledge – they don’t handle real-time knowledge.
2.2 Information Lake
A Information Lake can ingest uncooked knowledge as it’s. Not like an information warehouse, an information lake manages and offers methods to devour or course of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured knowledge. Ingesting uncooked knowledge permits an information lake to ingest historic and real-time knowledge in a uncooked storage system.
The information lake provides a metadata and governance layer, as proven within the following determine, to make the info consumable by the higher layers (stories, dashboarding, and knowledge mining). The next determine exhibits the structure of an information lake.

Fig. 2: The structure of an information lake
The primary benefit of an information lake is that it will probably ingest any sort of knowledge shortly because it doesn’t require any preliminary processing. The primary disadvantage of an information lake is that because it ingests uncooked knowledge, it doesn’t help the semantics and transactions system of the info warehouse.
2.3 Information Lakehouse
Over time, the idea of an information lake has developed into the info lakehouse, an augmented knowledge lake that features help for transactions at its high. In follow, an information lakehouse modifies the present knowledge within the knowledge lake, following the info warehouse semantics, as proven within the following determine.

Fig. 3: The structure of an information lakehouse
The information lakehouse ingests the info extracted from operational sources, comparable to structured, semi-structured, and unstructured knowledge. It offers it to analytics purposes, comparable to reporting, dashboarding, workspaces, and purposes. An information lakehouse includes the next important parts:
- Information lake, which incorporates desk format, file format, and file retailer
- Information science and machine studying layer
- Question engine
- Metadata administration layer
- Information governance layer.
2.4 Generalizing the Information Administration System Structure
The next determine generalizes the info administration system structure.

Fig. 4. The final structure of an information administration system
An information administration system (knowledge warehouse, knowledge lake, knowledge lakehouse, or no matter) receives knowledge as an enter and generates an output (stories, dashboards, workspaces, purposes, …). The enter is generated by individuals and the output is exploited once more by individuals. Thus, we will say that we now have individuals in enter and other people in output. An information administration system goes from individuals to individuals.
Individuals in enter embody individuals producing the info, comparable to individuals sporting sensors, individuals answering surveys, individuals writing a assessment about one thing, statistics about individuals, and so forth. Individuals in output can belong to one of many following three classes:
- Basic public, whose goal is to study one thing or be entertained
- Professionals, who’re technical individuals wanting to know knowledge
- Executives who make choices.
On this article, we are going to deal with executives since they generate worth.
However what’s worth? The Cambridge Dictionary provides totally different definitions of worth [2].
- The sum of money that may be obtained for one thing
- The significance or price of one thing for somebody
- Values: The beliefs individuals have, particularly about what is true and improper and what’s most necessary in life, that management their conduct.
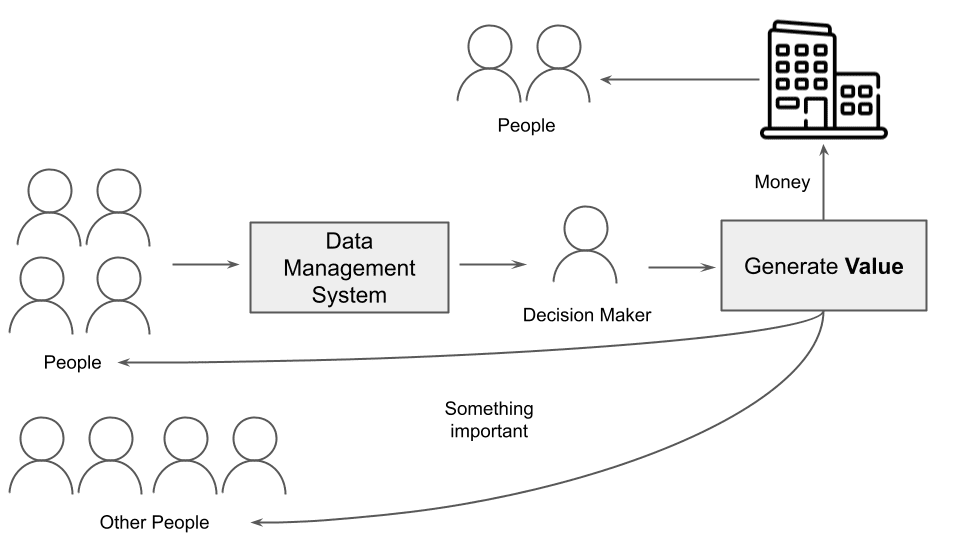
If we settle for the definition of worth because the sum of money, a choice maker may generate worth for the corporate they work for and not directly for the individuals within the firm and the individuals utilizing the providers or merchandise supplied by the corporate. If we settle for the definition of worth because the significance of one thing, the worth is important for the individuals producing knowledge and different exterior individuals, as proven within the following determine.

Fig. 5: The method of producing worth
On this state of affairs, correctly and successfully speaking knowledge to decision-makers turns into essential to producing worth. Because of this, your complete knowledge pipeline ought to be designed to speak knowledge to the ultimate viewers (decision-makers) with the intention to generate worth.
3. Information Storytelling
There are 3 ways to speak knowledge:
- Information reporting consists of knowledge description, with all the small print of the info exploration and evaluation phases.
- Information presentation selects solely related knowledge and exhibits them to the ultimate viewers in an organized and structured manner.
- Information storytelling builds a narrative on knowledge.
Let’s deal with knowledge storytelling. Information Storytelling is speaking the outcomes of an information evaluation course of to an viewers by a narrative. Primarily based in your viewers, you’ll select an acceptable
- Language and Tone: The set of phrases (language) and the emotional expression conveyed by them (tone)
- Context: The extent of particulars so as to add to your story, primarily based on the cultural sensitivity of the viewers
Information Storytelling should think about the info and all of the related info related to knowledge (context). Information context refers back to the background info and pertinent particulars surrounding and describing a dataset. In knowledge pipelines, this knowledge context is saved as metadata [3]. Metadata ought to present solutions to the next:
- Who collected knowledge
- What the info is about
- When the info was collected
- The place the info was collected
- Why the info was collected
- How the info was collected
3.1 The Significance of Metadata
Let’s revisit the info administration pipeline from an information storytelling perspective, which incorporates knowledge and metadata (context)

Fig. 6: The information administration pipeline from the info storytelling perspective
The Information Administration system includes two parts: knowledge administration, the place the primary actor is the info engineer and knowledge evaluation, the place the primary actor is the info scientist.
The information engineer ought to focus not solely on knowledge but additionally on metadata, which helps the info scientist to construct the context round knowledge. There are two sorts of metadata administration programs:
- Passive Metadata Administration, which aggregates and shops metadata in a static knowledge catalog (e.g., Apache Hive)
- Lively Metadata Administration, which offers dynamic and real-time metadata (e.g., Apache Atlas)
The information scientist ought to construct the data-driven story.
4. Information Administration and Information Storytelling
Combining Information Administration and Information Storytelling means:
- Contemplating the ultimate individuals who will profit from the info. A Information Administration system goes from individuals to individuals.
- Think about metadata, which helps construct essentially the most highly effective tales.
If we take a look at your complete knowledge pipeline from the specified consequence perspective, we uncover the significance of the individuals behind every step. We will generate worth from knowledge provided that we take a look at the individuals behind the info.
Abstract
Congratulations! You’ve gotten simply discovered how to have a look at Information Administration from the Information Storytelling perspective. You need to think about two facets, along with knowledge:
- Individuals behind knowledge
- Metadata, which provides context to your knowledge.
And, past all, always remember individuals! Information storytelling helps you take a look at the tales behind the info!
References
[1] IBM. What is data management?
[2] The Cambridge Dictionary. Value.
[3] Peter Crocker. Guide to enhancing data context: who, what, when, where, why, and how
Exterior assets
Using Data Storytelling to Turn Data into Value [talk]
Angelica Lo Duca (Medium) (@alod83) is a researcher on the Institute of Informatics and Telematics of the Nationwide Analysis Council (IIT-CNR) in Pisa, Italy. She is a professor of “Information Journalism” for the Grasp diploma course in Digital Humanities on the College of Pisa. Her analysis pursuits embody Information Science, Information Evaluation, Textual content Evaluation, Open Information, Net Purposes, Information Engineering, and Information Journalism, utilized to society, tourism, and cultural heritage. She is the creator of the e-book Comet for Information Science, printed by Packt Ltd., of the upcoming e-book Information Storytelling in Python Altair and Generative AI, printed by Manning, and co-author of the upcoming e-book Studying and Working Presto, by O’Reilly Media. Angelica can also be an enthusiastic tech author.





