Simulations illuminate the trail to post-event visitors move – Google Analysis Weblog
Fifteen minutes. That’s how long it took to empty the Colosseum, an engineering marvel that’s nonetheless standing as the most important amphitheater on the earth. Two thousand years later, this design continues to work effectively to maneuver huge crowds out of sporting and leisure venues.
However in fact, exiting the world is simply step one. Subsequent, individuals should navigate the visitors that builds up within the surrounding streets. That is an age-old drawback that continues to be unsolved to this present day. In Rome, they addressed the difficulty by prohibiting non-public visitors on the road that passes immediately by the Colosseum. This coverage labored there, however what in case you’re not in Rome? What in case you’re on the Superbowl? Or at a Taylor Swift live performance?
An strategy to addressing this drawback is to make use of simulation fashions, generally known as “digital twins”, that are digital replicas of real-world transportation networks that try and seize each element from the structure of streets and intersections to the move of automobiles. These fashions enable visitors consultants to mitigate congestion, scale back accidents, and enhance the expertise of drivers, riders, and walkers alike. Beforehand, our staff used these fashions to quantify sustainability impact of routing, test evacuation plans and present simulated visitors in Maps Immersive View.
Calibrating high-resolution visitors simulations to match the particular dynamics of a selected setting is a longstanding problem within the area. The provision of mixture mobility information, detailed Google Maps highway community information, advances in transportation science (resembling understanding the connection between segment demands and speeds for highway segments with visitors indicators), and calibration techniques which make use of pace information in physics-informed visitors fashions are paving the best way for compute-efficient optimization at a worldwide scale.
To check this expertise in the true world, Google Analysis partnered with the Seattle Division of Transportation (SDOT) to develop simulation-based visitors steering plans. Our aim is to assist 1000’s of attendees of main sports activities and leisure occasions depart the stadium space shortly and safely. The proposed plan diminished common journey journey occasions by 7 minutes for automobiles leaving the stadium area throughout massive occasions. We deployed it in collaboration with SDOT utilizing Dynamic Message Indicators (DMS) and verified impression over a number of occasions between August and November, 2023.
Simulation mannequin
For this undertaking, we created a brand new simulation mannequin of the world round Seattle’s stadiums. The intent for this mannequin is to replay every visitors state of affairs for a specified day as carefully as doable. We use an open-source simulation software program, Simulation of Urban MObility (SUMO). SUMO’s behavioral fashions assist us describe visitors dynamics, for example, how drivers make selections, like car-following, lane-changing and pace restrict compliance. We additionally use insights from Google Maps to outline the community’s construction and numerous static phase attributes (e.g., variety of lanes, pace restrict, presence of visitors lights).
 |
| Overview of the Simulation framework. |
Journey demand is a vital simulator enter. To compute it, we first decompose the highway community of a given metropolitan space into zones, particularly stage 13 S2 cells with 1.27 km2 space per cell. From there, we outline the journey demand because the anticipated variety of journeys that journey from an origin zone to a vacation spot zone in a given time interval. The demand is represented as aggregated origin–vacation spot (OD) matrices.
To get the preliminary anticipated variety of journeys between an origin zone and a vacation spot zone, we use aggregated and anonymized mobility statistics. Then we resolve the OD calibration drawback by combining preliminary demand with noticed visitors statistics, like phase speeds, journey occasions and vehicular counts, to breed occasion situations.
We mannequin the visitors round a number of previous occasions in Seattle’s T-Cellular Park and Lumen Discipline and consider the accuracy by computing aggregated and anonymized visitors statistics. Analyzing these occasion situations helps us perceive the impact of various routing insurance policies on congestion within the area.
 |
| Heatmaps reveal a considerable improve in numbers of journeys within the area after a sport as in comparison with the identical time on a non-game day. |
Routing insurance policies
SDOT and the Seattle Police Division’s (SPD) native data helped us decide essentially the most congested routes that wanted enchancment:
- Site visitors from T-Cellular Park stadium parking zone’s Edgar Martinez Dr. S exit to eastbound I-5 freeway / westbound SR 99 freeway
- Site visitors by Lumen Discipline stadium parking zone to northbound Cherry St. I-5 on-ramp
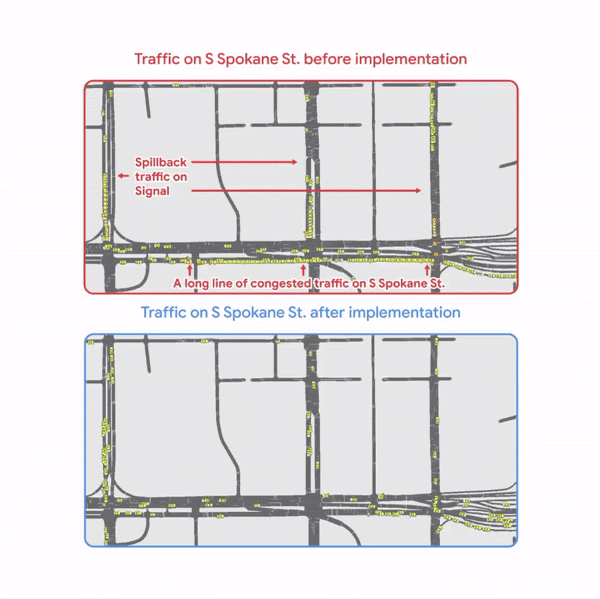
- Site visitors going southbound by Seattle’s SODO neighborhood to S Spokane St.
We developed routing insurance policies and evaluated them utilizing the simulation mannequin. To disperse visitors sooner, we tried insurance policies that will route northbound/southbound visitors from the closest ramps to additional freeway ramps, to shorten the wait occasions. We additionally experimented with opening HOV lanes to occasion visitors, recommending alternate routes (e.g., SR 99), or load sharing between completely different lanes to get to the closest stadium ramps.
Analysis outcomes
We mannequin a number of occasions with completely different visitors situations, occasion occasions, and attendee counts. For every coverage, the simulation reproduces post-game visitors and experiences the journey time for automobiles, from departing the stadium to reaching their vacation spot or leaving the Seattle SODO space. The time financial savings are computed because the distinction of journey time earlier than/after the coverage, and are proven within the beneath desk, per coverage, for small and enormous occasions. We apply every coverage to a share of visitors, and re-estimate the journey occasions. Outcomes are proven if 10%, 30%, or 50% of automobiles are affected by a coverage.
Based mostly on these simulation outcomes, the feasibility of implementation, and different issues, SDOT has determined to implement the “Northbound Cherry St ramp” and “Southbound S Spokane St ramp” insurance policies utilizing DMS throughout massive occasions. The indicators counsel drivers take various routes to achieve their locations. The mixture of those two insurance policies results in a mean of seven minutes of journey time financial savings per automobile, primarily based on rerouting 30% of visitors throughout massive occasions.
Conclusion
This work demonstrates the ability of simulations to mannequin, establish, and quantify the impact of proposed visitors steering insurance policies. Simulations enable community planners to establish underused segments and consider the consequences of various routing insurance policies, resulting in a greater spatial distribution of visitors. The offline modeling and on-line testing present that our strategy can scale back whole journey time. Additional enhancements will be made by including extra visitors administration methods, resembling optimizing visitors lights. Simulation fashions have been traditionally time consuming and therefore inexpensive just for the most important cities and excessive stake initiatives. By investing in additional scalable strategies, we hope to convey these fashions to extra cities and use instances world wide.
Acknowledgements
In collaboration with Alex Shashko, Andrew Tomkins, Ashley Carrick, Carolina Osorio, Chao Zhang, Damien Pierce, Iveel Tsogsuren, Sheila de Guia, and Yi-fan Chen. Visible design by John Guilyard. We wish to thank our SDOT companions Carter Danne, Chun Kwan, Ethan Bancroft, Jason Cambridge, Laura Wojcicki, Michael Minor, Mohammed Mentioned, Trevor Partap, and SPD companions Lt. Bryan Clenna and Sgt. Brian Kokesh.